Governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC) is an integrated framework that ensures an organization's adherence to established standards and regulations while managing risks effectively.
Traditionally, GRC processes have been manual, labor-intensive, and prone to human error. However, the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation technologies is revolutionizing these processes, marking a significant shift in how organizations approach GRC.
As we delve deeper into this article, we will explore AI's impact on various industries and how they set new governance, risk management, and compliance standards.
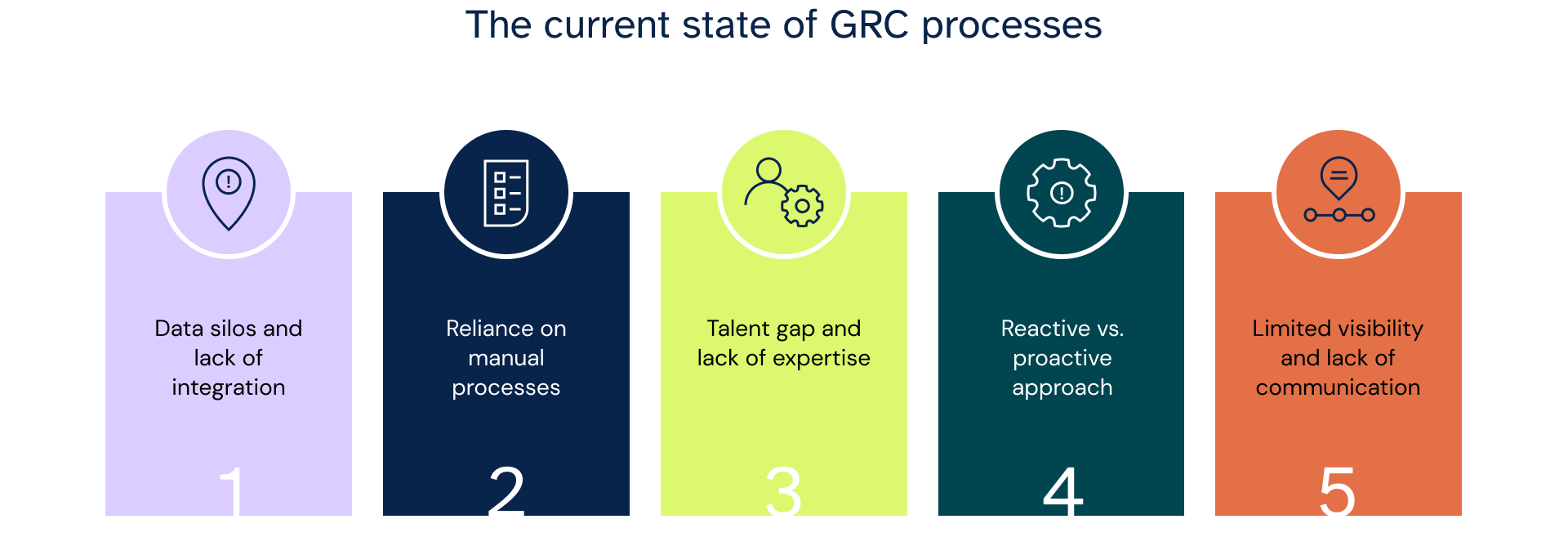
The current state of GRC processes
Today, the GRC processes are significantly transforming. Traditionally, GRC has been predominantly manual, involving extensive paperwork, data collection, and report generation. While foundational, this approach presents several challenges that modern organizations increasingly find untenable.
Manual GRC processes are inherently time-consuming. Compiling compliance reports, managing risk assessments, and maintaining governance protocols require significant human hours. This labor-intensive nature increases operational costs and diverts valuable resources from other critical areas. Additionally, manual processes depend on human input, making them susceptible to errors.
Data misinterpretations, transcription errors, and oversight in compliance requirements are common, posing a significant risk to the organization's integrity and compliance posture.
Data collection and analysis in a manual setting are also problematic. The growing volume and complexity of data organizations must handle today make manual processing inefficient and sometimes impractical. In modern regulatory compliance, accuracy and timeliness are paramount, so reliance on manual methods can lead to delays and inaccuracies in reporting.
Furthermore, manual GRC processes cannot keep up with the rapidly developing regulatory changes. Organizations are required to monitor and adapt to new regulations and standards continuously. Manual processes' slow and rigid nature makes this adaptation slower, potentially leading to non-compliance and associated risks.
With their understanding of these challenges, many organizations are turning towards automated solutions to streamline their GRC processes. By integrating technology, organizations aim to reduce the time and cost associated with manual processes while improving accuracy and compliance.
While traditional manual GRC processes are the foundation of many organizations' compliance and risk management strategies, their efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability limitations are increasingly apparent in today's fast-paced and data-driven business environment.

How AI is automating GRC
AI technologies can now automate and optimize most manual, repetitive tasks. That drives increased efficiency, cost savings, and proactive organizational risk management.
One key application of AI is collecting and analyzing data more efficiently. Organizations can train machine learning algorithms to rapidly gather, classify, and draw insights from large volumes of data across an organization. That includes emails, chats, documents, transaction records, sensor data, etc.
By processing and connecting data at scale, AI can spot real-time trends, patterns, and anomalies that indicate risks or non-compliance.
Another important use of AI is machine learning for proactively detecting potential issues and risks. Organizations can train machine learning models on the characteristics and patterns of known malware. These models can then scan new files and activity on a network to proactively detect if any software or files exhibit those malicious indicators. That allows quick identification of viruses, trojans, or spyware before they spread.
Natural language processing (NLP) also has many applications in automating GRC processes. Organizations can use NLP to rapidly analyze regulatory filings, laws, contracts, and internal policies to extract key information.
That helps assess compliance obligations and risks more efficiently compared to manual review. NLP models can also answer compliance queries by analyzing natural language questions and documents.
Organizations also use AI chatbots and virtual agents to handle GRC queries from staff, clients, and vendors. These bots can understand questions posed in natural language via chat and email and provide answers by referencing knowledge bases and regulations. Virtual agents can also collect information for compliance processes through conversational dialogue.
Finally, predictive analytics based on machine learning allows for data-driven forecasting of future risks. By analyzing past incidents and near-misses, models can identify potential issues before they occur. Predictive analytics provides powerful scenario modeling for proactive risk management in GRC.
While AI enables major improvements in automating GRC, there are still challenges to its adoption. These include upfront implementation costs, difficulties integrating AI with legacy systems, legal concerns around data privacy, and cultural resistance within organizations.
However, AI can significantly optimize GRC activities through automation with the right strategy to overcome these challenges.

Benefits of AI in GRC
Integrating AI into GRC has numerous benefits, fundamentally enhancing how organizations manage their governance, risk, and compliance programs. Some of the top advantages of implementing AI for GRC processes include:
Increased efficiency and productivity
One of the most significant advantages of implementing AI in GRC is the huge increase in efficiency and productivity. AI-powered tools automate tasks such as data collection, report generation, and compliance monitoring, which were traditionally manual and time-intensive. This automation translates into faster processing times and more accurate outcomes.
For instance, AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data in a shorter time than human employees, allowing for more timely responses to compliance requirements and risk assessments.
Cost savings from less manual work
The automation provided by AI leads to considerable cost savings. By reducing the reliance on manual labor for basic, repetitive tasks, organizations can allocate their human resources more strategically. That cuts operational costs and minimizes the risk of human error, which can be costly in terms of financial penalties and reputational damage.
Improved risk detection and compliance oversight
AI enhances risk detection and compliance oversight through advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms. These technologies can identify patterns and anomalies that indicate potential risks or compliance issues that go unnoticed in manual reviews. By providing more nuanced and comprehensive risk assessments, AI aids organizations in proactively managing potential threats.
More data-driven decision making
AI empowers organizations to make more data-driven decisions. By processing and analyzing large datasets, AI provides insights for strategic decisions regarding risk management and compliance strategies. This shift towards data-driven decision-making results in more informed, objective, and effective governance strategies.
Allows staff to focus on high-level oversight and strategy
One of the most transformative benefits of AI in GRC is freeing human resources to focus on high-level tasks. With AI handling the bulk of data processing and routine analysis, human staff can concentrate on more strategic aspects such as policy development, long-term risk management planning, and refining compliance frameworks. That optimizes the use of human talent and enhances the overall strategic direction of the organization's GRC efforts.
Deploying AI in GRC processes marks a huge step in how organizations approach governance, risk management, and compliance. By enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, improving risk detection and compliance, enabling data-driven decision-making, and allowing staff to focus on strategy, AI is setting a new standard in GRC.
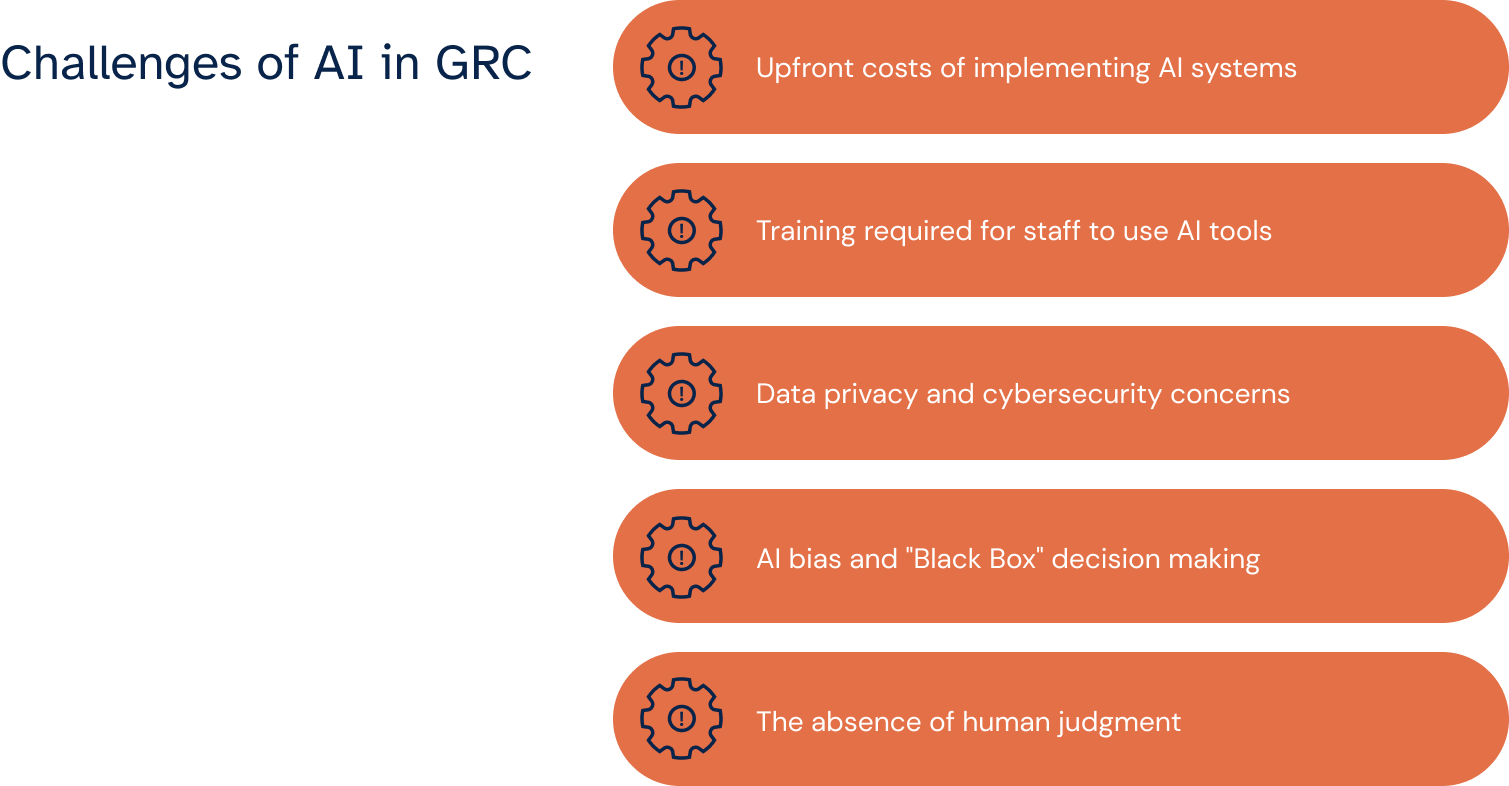
Challenges and limitations of AI in GRC
Incorporating AI into GRC processes may be significantly beneficial, but adopting and implementing it can be challenging and confusing. Here are some common challenges to its adoption:
Upfront costs of implementing AI systems
The initial investment in AI for GRC can be substantial. Implementing AI systems requires purchasing software and improving existing IT infrastructure to support these advanced technologies. This upfront cost can be a significant barrier, particularly for smaller organizations with limited budgets.
Training required for staff to use AI tools
Successfully deploying AI in GRC also depends on the staff's ability to use these tools effectively. That calls for comprehensive training programs to ensure employees are proficient in leveraging AI technologies. The time and resources required for this training can be considerable, adding to AI implementation's overall cost and complexity.
Data privacy and cybersecurity concerns
AI systems in GRC rely heavily on data, raising concerns about data privacy and cybersecurity. The vast amounts of sensitive data processed by AI tools must be safeguarded against breaches and unauthorized access, requiring robust cybersecurity measures.
AI bias and "Black Box" decision making
Another challenge is the potential for AI bias and the unclear nature of AI decision-making processes, often called the "black box" problem. AI systems learn from data, which means they can inadvertently perpetuate existing biases present in that data. In addition, understanding the rationale behind certain AI decisions can be difficult, which is problematic in the GRC industry, where transparency is crucial.
No replacement for human judgment
Finally, it's important to recognize that AI is no substitute for human judgment and discretion in GRC. While AI can process data and identify patterns at an unparalleled scale and speed, the nuanced understanding and ethical considerations in governance, risk management, and compliance still require a human touch.
While AI is significantly beneficial in streamlining and enhancing GRC processes, organizations must weigh these advantages against the challenges of high initial costs, extensive training, data privacy concerns, potential biases, and the irreplaceable value of human judgment.
Automating GRC processes with AI
As discussed, artificial intelligence plays a major role in transforming GRC through automation. AI enables more efficient data analysis, improved risk detection, faster regulatory review, and offers benefits like cost savings and productivity gains. While the future looks promising, AI cannot replace human judgment and discretion in GRC activities.
Organizations need a more comprehensive strategy to maximize AI's advantages while minimizing limitations. That includes investing in change management and training to onboard staff, implementing responsible AI practices, and taking an iterative approach to integrating AI in workflows.
Though some challenges remain, the outlook is bright for using AI to significantly enhance GRC through streamlined operations, proactive risk management, and improved regulatory compliance.
With an intelligent approach, companies can use AI to optimize GRC processes and strengthen their overall risk and compliance programs. That will better position them to take on complex regulatory and risk standards.
Experience a demonstration of how our AI-powered platform for cyber risk and compliance can help you.
Build a future where business governance, compliance, and risk management are more effective with 6clicks.
Written by Louis Strauss
Louis began his career in Berlin where he also founded Dobbel Berlin – Berlin’s curated search engine. Returning to Melbourne to join KPMG, Louis lead the development of software designed to distribute IP and create a platform for us by advisors and clients. While at KPMG, Louis also co-authored Chasing Digital: A Playbook for the New Economy. Louis is accomplished in stakeholder management, requirements gathering, product testing, refinement and project implementation. Louis also holds a Bachelor of Engineering and a Masters of Information Systems from the University of Melbourne.










