A quick review of GRC
Organizations have been dealing with increasingly complex Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) requirements for many years now. Not only are businesses struggling to keep up with the ever-changing regulatory and internal policies in order to remain compliant, but they also face daunting cyber security threats that place a further strain on GRC activities. Navigating these challenges can be a difficult task for any organization, especially when considering the hefty fines associated with non-compliance.
When it comes to tackling the challenges faced with GRC, organizations typically start by identifying which issues exist within their current process. Common problems include lack of real-time visibility into compliance activities, difficulty scaling frameworks across multiple departments or subsidiaries, inadequate IT security prowess and data privacy concerns. Additionally, manual audits and remediation processes are often used instead of automated solutions resulting in inefficient operations that cause significant delays in resolving problems. Despite the wealth of difficulties associated with GRC programs, there is hope yet if organizations commit to finding a comprehensive solution that will seamlessly scale their efforts to keep up with changing requirements and internal policies.
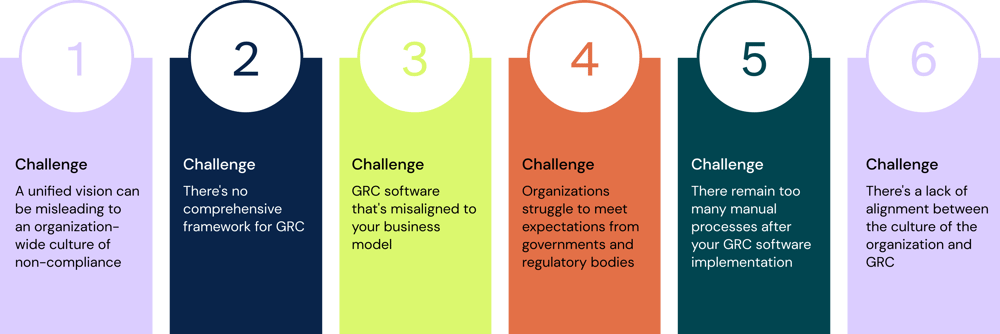
Challenge 1: A unified vision can be misleading to an organization-wide culture of non-compliance
Organizations today are struggling to keep up with an ever-changing and fluid set of compliance requirements. As regulatory and industry standards change, organizations must comply to meet these shifting demands, or face costly punishments for non-compliance. Unfortunately, too many silos exist within most companies’ infrastructure, hindering their ability to be compliant across the board. The cascading effect that results from the lack of unified processes creates further confusion; as each business unit or department operates independently and purchases their own technology and tools to solve specific problems or achieve objectives. Although this independent approach may bring short-term efficiency gains, it ultimately contributes to a culture of non-compliance when integrated reporting or transparency is lacking.
A unified vision can be misleading in such an environment because it fails to address the siloed nature of a company’s infrastructure in a meaningful way. Without effective integration between data, processes, technologies, stakeholders and reporting capabilities risk management programs meant for compliance are automatically weakened right out of the gate. To effectively combat this issue requires a top-down approach utilizing enterprise workflow software meant for commercially viable compliance solutions. Achieving true integration between business units then becomes possible while allowing for greater transparency throughout all departments of the organization; drastically reducing
This challenge is related to the approaches that do not consider the distributed and often complex nature of organizations which is explored further below.
Challenge 2: There's no comprehensive framework for GRC
The absence of a comprehensive governance, risk and compliance (GRC) framework can pose a significant challenge to business owners and executives who struggle to manage today's growing complexities. Without a clear and cohesive approach, organizations are more susceptible to legal issues, operational inefficiencies, waste of resources and the potential for damaging losses. To maximize operational performance, it is critical for businesses to build an effective GRC framework that brings together all aspects of risk identification and management within one well-defined system of integrated structures.
It is essential for companies to understand the type of risks that they face in order to properly respond to them. Strategic planning should be conducted with input from across the business at both the organizational level as well as departmental functions. Legal teams must be consulted appropriately on matters that affect compliance needs. Furthermore, proactive processes should be implemented that feature continuous auditing activities and periodic reviews of risk profiles. Organizations that have developed a comprehensive GRC framework can successfully identify their current exposures and identify areas in need of improvement - ultimately creating an agile structure for long-term success in a complex regulatory environment.
At a minimum, a comprehensive GRC framework needs to cater for the range of expectations organizations have in relation to GRC software such as:
- integrated vendor risk management;
- automated internal control processes;
- technical security controls to meet IT and cybersecurity related requirements;
- risk assessment processes integrated with your risk management methodology;
- Internal audit and associated remediation processes;
- a workflow-driven operational risk management process;
- an enterprise risk management process to help from the identification of potential risks to risk treatment; and
- continuous monitoring processes related to risks, regulation and audit.
These core capabilities will help you ensure a successful implementation and mitigate the increasing number of cyber risks, business risks and financial risks that are increasing in today's market.
Challenge 3: GRC software that's misaligned to your business model
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations often adopt distributed or federated business models to enhance flexibility, efficiency, and innovation. However, these decentralized structures can introduce a unique set of challenges related to governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC). Traditional GRC software may become misaligned with the needs of such business models, leading to potential inefficiencies and compliance gaps.
-
Lack of centralized visibility: In a distributed or federated model, decision-making authority is dispersed among different units or departments. Without a multi-tenanted GRC platform like 6clicks, with it's unique Hub & Spoke architecture, it becomes difficult for the management to have a holistic view of risk and compliance across the entire organization. This lack of visibility can result in blind spots, where potential risks are not adequately identified or addressed.
-
Inconsistent risk assessment and management: Distributed business models often mean that various units may employ different risk assessment methodologies or use separate GRC tools. This can lead to inconsistencies in risk evaluation, making it challenging to compare and prioritize risks across the organization. The absence of a unified approach can result in resources being allocated inefficiently, focusing on less critical risks while more significant threats remain unattended.
-
Difficulty in standardizing compliance practices: Compliance requirements may vary depending on the industry, location, or business unit. In a distributed model, adhering to a consistent set of compliance standards becomes complex without a GRC solution that can accommodate the need for central control and autonomous team needs. This can expose the organization to compliance violations, penalties, and reputational damage due to the lack of standardized practices and controls.
-
Fragmented reporting and communication: Effective communication and reporting are crucial in a distributed or federated model to ensure that risk-related information reaches the relevant stakeholders promptly. Communication channels might be fragmented, leading to delays, misunderstandings, and a decreased ability to respond quickly to emerging risks or compliance issues.
-
Increased resource overhead: In the absence of a multi-tenanted GRC platform, organizations might end up using multiple software applications to manage risk, compliance, and governance across different units. This can result in increased costs related to software licensing, training, and maintenance. Additionally, managing disparate systems can be resource-intensive and reduce overall efficiency.
-
Limited collaboration and knowledge sharing: A distributed business model can hinder collaboration and knowledge sharing between various units. A platform like 6clicks can facilitate a collaborative approach to risk management, enabling business units to share best practices, insights, and lessons learned from their experiences.
-
Difficulty in scaling GRC efforts: As organizations grow, managing risk and compliance becomes more complex. Scaling GRC efforts without a centralized solution can lead to inconsistencies and difficulties in adapting to new regulatory requirements or industry standards.
The illustration below highlights what is possible with a multi-tenanted GRC approach.
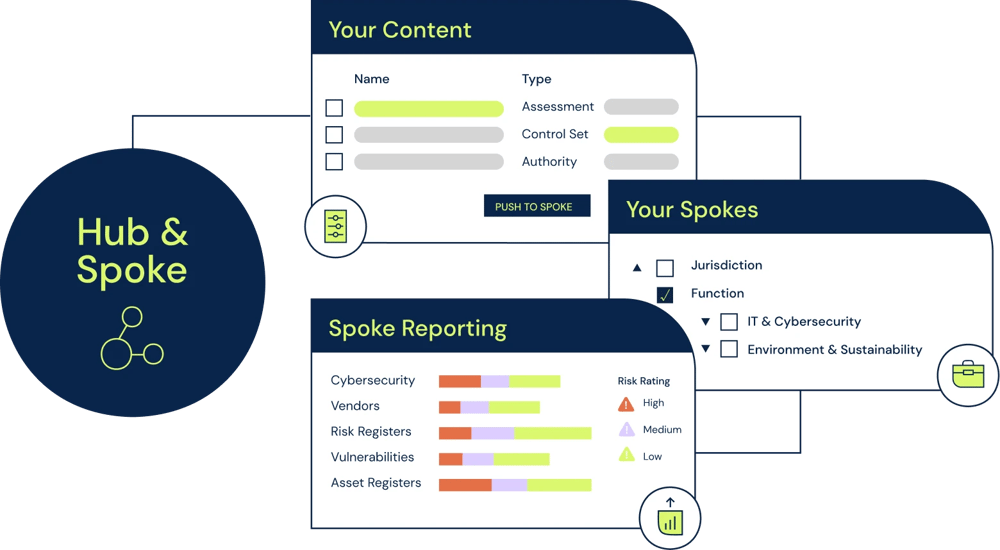
Learn more about 6clicks' unique Hub & Spoke design for federated businesses here.
Challenge 4: Organizations struggle to meet expectations from governments and regulatory bodies
Maintaining compliance with governmental and regulatory organizations is an important part of doing business in today’s world. With risk and compliance mandates increasing all the time, it’s essential that organizations have a strong understanding of their obligations and are able to meet them consistently.
Rather than placing all of the burden on just one area or department within the organization, it’s important for this responsibility to run through every segment of the business. From putting firm policies and procedures in place to keeping up to date with new regulations, taking a proactive approach across all areas ensures that each layer of the business is adequately prepared for any possible changes or challenges. This type of compliance can also help shape organizational culture by giving everyone in the company confidence that they are adhering to proper protocols and standards. Additionally, by building strong links between departments it makes it easier for GRC requirements to be seamlessly integrated into existing process so new rules can be managed swiftly and efficiently without disruption.
Challenge 5: There remain too many manual processes after your GRC software implementation
GRC processes have traditionally relied upon manual processes and disparate tools to generate insights, leading to an inefficiency that renders enterprises unable to meet compliance mandates. The inherent risk associated with a lack of visibility to ongoing GRC management is amplified not only due to archaic processes across spreadsheets, emails, phone calls, and teams but also because they do not provide any kind of intelligence.
For businesses with multiple IT systems supporting operations, the lack of accountability and follow through by having no audit trail can open up enterprises for the potential of fabrication or deception. Without proper tracking, it’s impossible for any enterprise staff to immediately identify who is reviewing what items and taking the necessary action without going down a long list that could be outdated. In addition, manual GRC reviews impede an organization's ability to respond quickly and proactively in today's ever-changing regulatory landscape as these processes are highly laborious and restrictive.
Challenge 6: There's a lack of alignment between the culture of the organization and GRC
A lack of alignment between the culture of the organization and GRC (Governance, Risk and Compliance) is becoming an increasing problem. With today’s stringent compliance regulations, organizations must have a comprehensive GRC strategy in place. They must understand the need for combining people, compliance with technology and ensuring employees are aware of clear processes they can follow to make sure the company remained compliant with applicable regulations. However, if not implemented properly, it may lead to expensive fines or serious reputational damage.
Top-level executives must be the catalyst to initiate transformation within a corporate culture that takes risk and compliance management seriously. Achieving this requires education on different aspects of governance across all levels, from making sure everyone is aware of their company’s policies to actually putting those policies into practice. Information should be disseminated across all tiers so that there is buy-in amongst all stakeholders involved. It might take some time to completely develop an effective GRC strategy as well as shift current mindsets; however, with commitment from key decision makers and appropriate processes put into action, it is possible to see positive change in an organization’s terms of GRC adherence over time.
How organizations can address these challenges?
Businesses can address the challenges above is to invest in a modern GRC platform to better manage structures across the whole GRC architecture. For example, businesses can consider leveraging automated processes and systems which would enable them to quickly establish important facts and take appropriate action if needed. Such automation also allows businesses to identify weaknesses in their risk management plans well ahead of time before any real damage is caused by external or internal factors. Accessing comprehensive data points related to risk issues along with accurate insights from experienced professionals can also help provide effective solutions for successful GRC management journeys for different practices, procedures, policies, technologies, operations, and external business partners.
If you are looking for a modern GRC platform, with all the functionality you need to support a comprehensive GRC framework, please check out information about the 6clicks platform here.
Written by Anthony Stevens
Ant Stevens is a luminary in the enterprise software industry, renowned as the CEO and Founder of 6clicks, where he spearheads the integration of artificial intelligence into their cybersecurity, risk and compliance platform. Ant has been instrumental developing software to support advisor and MSPs. Away from the complexities of cybersecurity and AI, Ant revels in the simplicity of nature. An avid camper, he cherishes time spent in the great outdoors with his family and beloved dog, Jack, exploring serene landscapes and disconnecting from the digital tether.